Call us +918978574081, 7731064081.
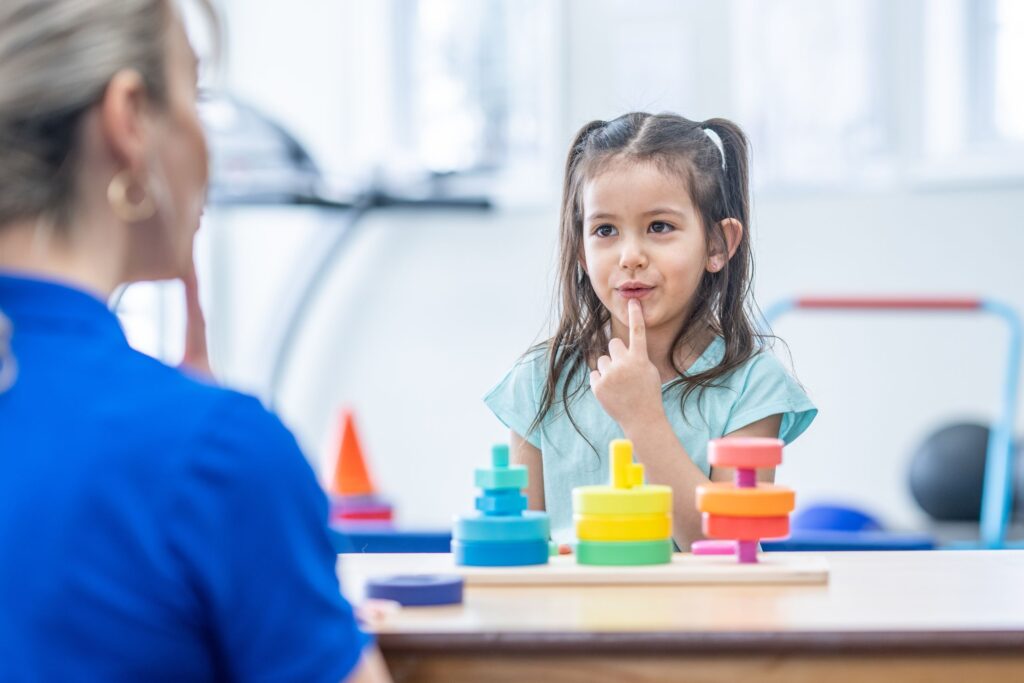

1) What is Speech Therapy?
A)Speech therapy for children is a specialized treatment aimed at diagnosing, assessing, and improving communication and speech disorders. It focuses on helping children develop effective speaking, understanding, and social communication skills. Speech therapy addresses a range of issues such as difficulties with pronunciation (articulation), language comprehension and expression, fluency problems like stuttering, voice disorders, and swallowing difficulties.
(1.1)What are first words of speech in child?
A)The first words of speech in a child typically appear between 10 and 14 months of age. The most common first words are usually related to people and objects frequently encountered in the child’s daily life, such as “mama,” “dada,” “ball,” “dog,” “hi,” “bye,” and “no.” These early words often involve easy mouth movements, like bringing the lips together or placing the tongue behind the upper teeth (“mama” and “dada”) because these motions are simpler for babies to make and relate to early sensory feedback during feeding.In summary, common first words are simple, emotionally significant, and often social words like “mama,” “dada,” “hi,” and “bye” that a child uses consistently around the age of one year.
(1.2) What are the common words of speech in 1 year baby?
A)Common words of speech for a 1-year-old baby typically include simple and familiar terms. By around 12 months, most babies say one or two words like “mama,” “dada,” “hi,” “bye,” “dog,” and “uh-oh.” These words may not always be clear but generally refer to people, objects, or events important to the child. Other common early words include “ball,” “baby,” “no,” “bottle,” “woof woof,” “banana,” and simple sounds that mean something consistent to the child, such as “ba-ba” for bottle or “moo” for milk. Here are some examples of typical words spoken by a 1-year-old baby:Family member names: mama, dada, papaSocial words: hi, bye, no, uh-ohObject names: ball, dog, baby, bottle, bananaAnimal sounds: woof woof, mooCommon sounds with meaning: ba-ba (bottle), nana (banana)At this age, communication is a mix of words, sounds, and gestures, as toddlers begin to understand and use language to express themselves.
1.3 )Speech Development and Stages in Child?
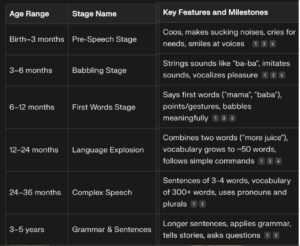
2)What is Speech Delay ?
A)Speech delay in children is a condition where a child does not develop speech and language skills at the expected rate for their age. Speech refers to the physical act of producing sounds and words, while language involves understanding and using words to communicate. A child with speech delay might use words or phrases but be difficult to understand or may struggle to form sounds properly. This delay can involve problems with articulation, oral-motor skills (such as coordinating lips, tongue, and jaw), or comprehension and expression of language. Causes of speech delay include oral impairments, hearing problems, brain areas affecting speech muscles, developmental disorders like autism, and sometimes no clear cause is identifie.
3). What are the Milestones in Speech?
A)Speech milestones refer to the typical developmental stages and skills related to speech and language that children achieve as they grow. These milestones help track how children progress in their ability to understand and use language, including sounds, words, sentences, and communication gestures. They serve as a guide to identify if a child is developing speech and language skills appropriately for their age or if there might be delays or issues requiring assessment.Speech milestones cover a range of ages from birth to about 5 years, and include behaviors such as responding to sounds, cooing, babbling, saying first words, understanding simple commands, forming sentences, and engaging in conversations. Milestones are commonly grouped by age ranges, for example:
1. Birth to 3 months: recognizing voices, different cries, cooing sounds
2. 4 to 6 months: responding to sounds and tone changes, babbling
3. 7 to 11 months: responding to name, babbling characteristic sounds, using gestures
4. 12 to 24 months: saying first words, understanding simple commands, combining two words
5. 2 to 3 years: using simple sentences, following two-step commands, naming objects
6. 3 to 4 years: using several hundred words, describing objects, answering questions
7. 4 to 5 years: understanding complex questions, using longer sentences, engaging in storytelling.
4)what are the equipments used in speech therapy?
A)Speech therapy uses a variety of specialized equipment designed to improve speech, articulation, language processing, fluency, and oral motor skills. Here are some common and effective equipment used in speech therapy:
Specialized Tools for Articulation and Oral Motor Skills
• Speech Buddies: Devices that help position the tongue correctly to produce specific sounds such as “l,” “r,” “s,” “sh,” and “ch.”
• Talktools Bilabial Shapes: Different shapes to practice bilabial sounds like “m,” “p,” and “b” using visual and tactile feedback.
• Talktools Tactile Tubes: Aid in vowel production by helping with lip rounding and tactile feedback.
• Talktools Apraxia Blocks: Color-coded bite blocks that improve jaw stability for vowel sounds, helpful for apraxia.
• Talktools Horn and Straw Kits: Tools to enhance airflow control and lip, tongue, and jaw movements essential for sound production.
• Chewy Tubes: For oral sensory stimulation and strengthening jaw muscles.
• Tongue Tip Elevation/Lateralization Tools: Help practice tongue movements for sounds like “t,” “d,” “n,” and “l.”
• Tongue Depressors: Used for jaw stability and lip closure exercises.
• Nose Flute: Helps with nasal sounds and encourages nasal airflow.
Common Therapy Aids and Technology
• Mirrors: To allow patients to see their mouth and tongue movements for correct sound production.
• Picture Cards and Visual Aids: Help with word and sound pronunciation through visual association.
• Adaptive Communication Switches: Devices for non-verbal patients to assist in communication.
• Tablets and Apps: Interactive software and apps that engage patients in sound and word practice.
• Voice and Video Recorders: For feedback and monitoring progress during sessions.
Other Materials
• Story cards, puppets, toys, and games are often used for language processing and engagement, especially with children.
5). What Are The Techniques Used In Speech Therapy?
A). There are several different types of speech therapy methods, each tailored to address specific speech and communication difficulties. The main types include:
1.Articulation Therapy: Focuses on improving the clarity and accuracy of speech sounds by practicing sound production and coordinating articulatory movements of lips, tongue, and jaw for correct pronunciation.
2.Language Therapy: Aims to enhance understanding and use of language, including vocabulary, grammar, comprehension, and expression through activities like storytelling and structured exercises.
3.Fluency Therapy: Helps individuals who stutter or have disruptions in speech flow by using breathing exercises, relaxation, and speech modification techniques to promote smoother speech.
4.Voice Therapy: Addresses issues related to vocal quality, pitch, volume, and resonance with exercises to strengthen vocal muscles and develop healthy vocal habits.
5.Oral Motor Therapy: Strengthens muscles involved in speech and swallowing through exercises such as blowing, sucking, and chewing.
6.Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC): Uses tools and strategies like picture exchange communication to aid communication for those with severe speech impairments.
7.Specialized Methods: Including VitalStim Therapy for swallowing disorders using electrical stimulation, Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT) for improving speech volume, and cognitive-communication therapy for adults with brain injuries or degenerative conditions.
These methods can be customized according to the individual’s needs, age, and type of speech disorder and may be used in combination for effective treatment .
6). What Are The Speech Tools, Used For Autism Kids ?
A). Speech tools, specifically in the context of speech therapy, are specialized devices or aids used to help individuals improve their communication skills. These tools provide tactile, visual, and auditory cues that support the correct production of speech sounds by guiding the movements of the tongue, lips, and jaw. They go beyond traditional speech therapy by engaging multiple senses and making the learning process easier and faster.
For autism, speech tools and therapy aim to address the unique challenges in communication that individuals on the spectrum face. Autism speech therapy helps improve verbal, nonverbal, and social communication skills. Speech therapy tools for autism can include:
1. Speech Buddies: Tools that help target specific sounds by guiding tongue placement.
2. Talktools: A variety of tools assisting with specific sounds (bilabial shapes, tactile tubes, apraxia blocks, tongue tip tools) and oral motor skills.
3. Chewy Tubes: Used for oral sensory stimulation and strengthening jaw muscles.
4. Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) devices: Technology and apps that aid nonverbal autistic individuals in communicating.
5. Visual supports like picture exchange cards and storyboards to aid understanding and expression.
6. Play-based techniques to improve social communication through interactive play.
Speech therapy for autism typically focuses on improving speech clarity, expressive and receptive language, social communication skills, and alternative communication methods if needed. It involves personalized goals based on evaluations and aims to empower individuals to communicate more effectively in daily life.
In summary, speech tools for autism are varied and designed to enhance different aspects of communication, from articulation and oral muscle control to alternative communication methods for nonverbal individuals, facilitating both speech and social interaction improvements.
Speech tools, especially in the context of speech therapy, are specialized aids designed to improve communication skills by helping with correct tongue, lip, jaw placements, and airflow control to produce speech sounds clearly. These tools provide tactile and kinesthetic feedback, making it easier for individuals to learn and master specific sounds and overcome speech challenges like articulation issues, apraxia, oral sensory problems, and jaw stability.
Popular Speech Therapy Tools and Their Uses
1. Speech Buddies: Help with sounds such as “l”, “r”, “s”, “sh”, “ch” by guiding tongue placement.
2.Talktools Bilabial Shapes: Assist with bilabial sounds like “m”, “p”, and “b” using tactile and visual cues.
3.Talktools Tactile Tubes: Aid in vowel production by helping with lip rounding, especially useful for apraxia and poor muscle tone.
4. Talktools Apraxia Blocks: Stabilize the jaw to improve vowel sound production.
5. Talktools Horn Kit: Enhances airflow control necessary for speech fluency.
6. Chewy Tubes: Strengthen jaw muscles and improve oral sensory skills.
7. Talktools Tongue Tip Elevation/Lateralization Tool: Helps with precise tongue movements for sounds like “t”, “d”, “n”, and “l”.Nose Flute: Trains nasal airflow critical for nasal sounds like “m” and “n”.
7). What Is Articulation Speech Therapy In Autism ?
A). Articulation therapy in speech for autism is a specialized intervention aimed at improving a child’s ability to produce specific speech sounds correctly, thereby enhancing speech intelligibility. It involves systematically practicing target sounds starting from isolation (the sound by itself), then progressing through syllables, words, sentences, stories, and finally conversation to generalize clear speech across contexts. Therapists utilize techniques such as vocal imitation, prompting, shaping, and sometimes physical cues for tongue and lip placement to help children with autism practice and master the articulation of challenging sounds.
Children with autism may have articulation difficulties as part of broader speech sound or oral-motor challenges. Articulation therapy addresses sounds they struggle with by breaking down the learning process into steps and using methods that fit their unique learning styles. This therapy is important because many children with autism have speech that is hard to understand, which can impact communication and social interaction. Articulation therapy helps increase their spoken clarity, facilitating better communication with others.
Key components of articulation therapy include isolation of sounds, practicing sounds in syllables and words, constructing sentences with target sounds, telling stories using these sounds, and engaging in conversations to ensure skill generalization. Therapists often make therapy engaging using games, interactive apps, and fun exercises tailored to the child’s interests and abilities.
In summary, articulation therapy for autism focuses on improving the accuracy and clarity of speech sounds through structured, evidence-based, and often individualized practice, helping children with autism enhance their functional speech communication.
9). What Is Echolalia Speech In Autism?
A). Echolalia in autism speech refers to the repetitive speech pattern where individuals with autism repeat words, phrases, or sounds they have heard, either immediately or after some delay.
autistic individuals and serves several important functions, including aiding language development, facilitating social interaction, expressing emotions, and providing comfort or self-regulation.
There are two main types of echolalia:
1. Immediate Echolalia: repeating words or phrases immediately after hearing them.
2. Delayed Echolalia: repeating words or phrases after a time delay, sometimes days or months later.
Echolalia can seem like meaningless repetition, but for autistic individuals, it is often a functional and adaptive communication strategy.
It helps them practice language, understand sentence structures, and can be used as a tool to communicate, self-stimulate, cope with stress, or connect socially. Recognizing echolalia as a purposeful form of communication is important.
10). Is Echolalia Can Occur Only In Autism Kids (Or) ADHD Kids ?
A). Echolalia, the repetition of words or phrases spoken by others, is more commonly associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) but can also occur in individuals with ADHD. However, echolalia is not a defining characteristic or diagnostic criterion for ADHD, whereas it is much more prevalent in autism, with approximately 75–80% of people with ASD exhibiting echolalia at some point in their development. Echolalia in ADHD may result from cognitive or behavioral difficulties such as impulsivity, challenges with attention, or co-occurring neurodevelopmental conditions, but its presence alone does not indicate either autism or ADHD—a comprehensive assessment is necessary for proper diagnosis.
Echolalia in Autism
1. Echolalia is very common in autism spectrum disorder and is considered a key feature, often serving as a communication strategy when individuals cannot generate their own language.
2. Children with autism may use echolalia for a longer period and more frequently than neurotypical peers or children with other conditions.
Echolalia in ADHD
1. Though not a core symptom, echolalia may manifest in some individuals with ADHD due to impulsivity, attention deficits, or as a coping mechanism for sensory processing challenges.
2. Language and communication difficulties are not central to ADHD, so echolalia is usually observed when there is a comorbid neurodevelopmental issue such as ASD.
3. About 50–70% of people with ASD may also have ADHD, leading to some overlap in symptoms and presentations.
11). What is Stammering / Stuttering In Speech ?
A). Developmental, neurogenic, and psychogenic stuttering differ primarily in their causes, onset, symptoms, and treatment approaches:
1. Developmental Stuttering occurs in early childhood (ages 2 to 5) linked to typical speech and language development. It features repetitions, prolongations, and blocks, fluctuates depending on speaking situations, and may improve over time or with therapy. Anxiety can exacerbate it. Treatment mainly involves speech therapy and family support.
2. Neurogenic Stuttering results from brain injury, stroke, or neurological diseases affecting the brain areas controlling speech. It can appear at any age after neurological events and is characterized by consistent disfluencies regardless of speaking context. It is typically accompanied by other neurological symptoms. Treatment focuses on speech motor reprogramming, fluency shaping, and rehabilitation.
3. Psychogenic Stuttering stems from psychological trauma, stress, or mental health disorders rather than neurological damage. Its onset is often sudden and related to stress or trauma, with speech disfluencies that may fluctuate with emotional state. Unlike developmental stuttering, affected individuals may show little concern (“la belle indifference”). Treatment emphasizes psychotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and supportive speech therapy.
Stammering speech, also known as stuttering, is a speech disorder marked by disruptions in the normal flow and rhythm of speech.involves repeating sounds or syllables (e.g., “mu-mu-mummy”), prolonging sounds (e.g., “mmmmummy”), or getting stuck on words and being unable to produce them. Stammering can vary in severity and may come and go depending on the situation.There are two main types of stammering:Developmental stammering: This is the most common type, occurring in early childhood as speech and language skills develop.Acquired or late-onset stammering: This is rarer and can result from head injuries, strokes, neurological conditions, certain medications, or psychological trauma.
Common symptoms include repeating or stretching out sounds, difficulty starting words, blocks where words get stuck, physical tension or struggle when speaking, and anxiety around speaking. Stammering may worsen in stressful situations or when feeling hurried.
12). What Is Motor Speech Disorder ?
A). Motor speech disorder is a neurological condition that affects an individual’s ability to plan, program, control, coordinate, and execute speech production, primarily due to impairments in the nervous system . These disorders disrupt the body’s natural capacity to speak, often resulting from damage or dysfunction to the central or peripheral nervous systems.
Types of Motor Speech Disorders
1. Dysarthria: Characterized by slow, imprecise, and distorted speech caused by weakness or incoordination of the muscles used for speech, such as the tongue, lips, and voice box. It results from neurological damage affecting muscle control, which can be due to stroke, head injury, or degenerative diseases
2. Apraxia of Speech: Involves difficulty in planning and sequencing the movements necessary for speech, despite having normal muscle strength. It can be congenital (childhood apraxia) or acquired after neurological injury like a stroke, with difficulties including slow speech and irregular sound errors .
13). What Are The Types Of Speech Disorders In Child ?
A). Types of speech disorders in English include a variety of conditions that affect a person’s ability to produce sounds, speak smoothly, or use their voice correctly. Common types are:
1. Apraxia of Speech: Difficulty in coordinating the movements needed for speech, often due to neurological issues.
2. Dysarthria: Weakness or paralysis of the speech muscles, resulting in slurred or slow speech.
3. Stuttering: Interruptions in the flow of speech such as repetitions, prolongations, and blocks.
4. Speech Sound Disorders: Issues with producing specific speech sounds correctly, including articulation disorders (physical difficulty in making sounds) and phonemic disorders (difficulty understanding sound distinctions).
5. Voice Disorders: Problems with the vocal cords or larynx causing hoarseness, breathiness, or inability to speak.
6. Aphasia: Language disorder causing difficulty in comprehension or expression of speech.Cluttering: Rapid and/or irregular speech making it hard to understand.
7. Lisps: Difficulty in pronouncing sibilant sounds like /s/ and /z/.
8. Muteness: Complete inability to speak.
14). What Are The Activities Involve In Speech ?
A). The activities involved in speech include various interactive and practical exercises designed to enhance verbal and nonverbal communication skills. These activities aim to improve clarity, vocabulary, listening, expression, and confidence in speaking. Some common speech-related activities are:
1. Impromptu Speaking: Speaking spontaneously on a given topic to practice quick thinking and clear expression.
2. Storytelling and Continuous Story: Participants create or continue a story aloud, fostering creativity and narrative skills.
3. Debates: Structured discussions where participants argue different viewpoints, building critical thinking and persuasion.
4. Telephone Game (Chinese Whispers): A message is passed by whispering in a line, highlighting listening and clarity in communication.
5. Charades with a Twist: Acting out words or phrases to enhance nonverbal communication.
6. Interview Role Play: Practicing interview questions to improve conversational and formal speech skills.
7. Picture Storytelling: Using images to create and narrate stories, boosting descriptive language and imagination.
8. Stand Up for Fillers: Speaking on topics while avoiding filler words, which encourages precise and effective language use.
9. Listening and Following Directions Games: Activities such as Blindfold Instructions develop verbal guidance and listening skills.
10. Emotion and Expressive Reading: Reading sentences with varying emotions to enhance emotional intelligence in speech.
15). What Is The Role & Involvement Of Perents To Improve Early speech In Their Kids ?
A). Parents play a crucial and multifaceted role in improving early speech and language development in their children. Their involvement includes providing rich and responsive language input, engaging in meaningful interactions, participating actively in learning activities like shared book reading, and reinforcing speech therapy techniques at home. Both the quantity and quality of parental speech, along with sensitive and timely responsiveness to the child’s communicative attempts, are key factors in fostering early language skills.
Key Roles and Involvement of Parents
1. Quantity and Quality of Speech: Parents who frequently talk to their children, using diverse and complex vocabulary, significantly boost children’s vocabulary growth and language skills. The richness of language, not just the amount spoken, is a strong predictor of early speech development .
2. Responsive Interactions: Engaging in reciprocal “serve and return” interactions, where parents attentively respond to their child’s vocalizations, gestures, and expressions, supports active communication development. These sensitive and responsive exchanges help children learn proper communication patterns .
3. Routine Learning Activities: Consistent participation in shared activities such as book reading, storytelling, and conversational engagements provides a critical foundation for language and literacy skills. These activities expand vocabulary, comprehension, and emergent literacy .
4. Parental Involvement in Speech Therapy: For children receiving speech therapy, parents play a pivotal role by practicing therapy techniques at home during everyday routines, which reinforces the child’s learning and accelerates progress. Parental observations and feedback also help tailor therapy more effectively .
5. Father’s Role: Fathers’ language input, especially during infancy, uniquely contributes to expressive language development. Fathers’ use of diverse vocabulary in early interactions supports better communication outcomes, complementing maternal contributions .
16). In Which Age The Early speech Starts In Child ?
A). Early speech in children typically starts around 6 months with babbling sounds such as “ooh,” “aah,” and “ba-ba.” Babies usually say their first meaningful words between 12 and 18 months of age. By the age of 12 months, some babies may say “ma-ma” or “da-da,” and between 18 to 24 months, toddlers often begin to combine two to three words into simple phrases. Speech development continues rapidly after that, with vocabulary expanding significantly by age 2 and more complex sentences forming by age 3 .
Early Speech Milestones
1. Birth to 3 months: Babies make cooing sounds, respond to voices, and express with sounds like laughter or fussing.
2. 4 to 6 months: Babbling begins (repeating sounds such as “ba-ba”).
3. 7 to 11 months: Imitation of simple words and babbling continues.
4. 12 to 18 months: First meaningful words generally appear (e.g., “mama,” “dada”).
5. 18 to 24 months: Two to three-word phrases begin to emerge.
6. By age 2: Vocabulary typically grows to 50 or more words.By age 3: Children use three to four-word sentences and are understood by familiar people .
This timeline may vary among children, but these are typical age ranges for the emergence of early speech.
18). What Are The Reasons For Speech Dealy In Autism , ADHD , Mr And Down Syndrome Children ?
A). Children with autism, ADHD, mental retardation, or Down syndrome may not speak or may have delayed speech for different neurological and developmental reasons tied to their conditions.
For children with autism:
1. They often face challenges with speech and language development, including delayed onset or absence of spoken language. This is due to difficulties in social communication, challenges understanding non-verbal cues, and atypical brain development affecting language areas. Some children use echolalia (repeating words or phrases) or have unusual speech patterns such as monotonous or robotic speech. Social communication impairments are core features of autism that severely affect verbal communication ability .
2. Speech and Language Therapy (SLT) can help improve their communication through various supportive techniques, but some remain non-verbal or minimally verbal .
For children with ADHD:
1. Speech delays are less typical but can occur if attention deficits interfere with language learning and social interaction. Also, hyperactivity and impulsivity may impact the focus needed for speech acquisition. Speech problems are usually less severe than in autism or intellectual disabilities.
For children with mental retardation (intellectual disability):
1. There is a generalized delay in acquiring speech and language due to impaired cognitive development affecting understanding and expressive language. This results in limited vocabulary and difficulties in forming sentences proportional to their cognitive level.
For children with Down syndrome:
1. Speech issues arise from a combination of low muscle tone affecting oral motor skills, hearing loss, and cognitive delay. These children typically have delayed speech onset and difficulties articulating sounds clearly, leading to less verbal communication .
In summary, the lack of speech in these children stems from neurological and developmental factors affecting social communication, cognitive understanding, motor speech abilities, and attention mechanisms. Each condition has distinct pathways but may share overlapping communication challenges that require specialized therapies to support speech and language development.
19).what Is Importance For Children with Speech Dealy , Either Speech Therapy (or) Normal Schooling ?
A). Speech therapy is generally more important than relying on “normal” (mainstream-only) schooling alone for children with speech delay, because targeted assessment and intervention directly address underlying communication needs that classrooms usually cannot fully provide.
Why speech therapy matters
1. Speech therapy gives a tailored diagnosis and treatment plan for the child’s specific problem (articulation, expressive language, receptive language, apraxia, stuttering, or voice issues), which mainstream classrooms rarely provide in depth.
2. Early, targeted intervention takes advantage of rapid brain and language development in the preschool years and improves long‑term outcomes in language and literacy when started early.
3. Clinical evidence shows therapy produces measurable gains for many types of speech problems (notably phonological and vocabulary deficits), while classroom exposure alone often fails to close those gaps .
Limits of mainstream schooling alone
1. Regular classrooms provide important social models and exposure to language, but they usually lack the frequency, intensity, and individualized methods that many children with speech delay need to make clinical progress .
2. Studies and reviews report that mainstream provision without integrated, consistent speech-language support often results in smaller gains and unmet needs for children with significant language disorders .
Best-practice approach (recommended)
1. Combine speech-language therapy with inclusive schooling: obtain a formal speech-language assessment, start individualized therapy (clinic, school-based, or integrated) and ensure classroom supports (IEP/accommodations, visual supports, small-group pull-outs) to generalize skills across settings .
2. Begin early and monitor progress regularly; involve caregivers in home practice because parent-implemented strategies boost outcomes similarly to clinician-delivered work in many cases .
3. If mainstream schools cannot provide adequate individualized support, consider specialist provision or additional therapy hours until the child reaches functional communication and academic readiness
Practical next steps
1. Get a speech-language pathologist (SLP) evaluation as soon as concerns arise to determine type and severity of delay .
2. Ask the school for an evaluation and an individualized plan (IEP or equivalent) that includes direct SLP time and classroom accommodations .
3. Start home strategies recommended by the SLP (modeling, expanded language, play-based routines) and schedule regular progress reviews.
20). What Are The Main Reasons Of Speech Problems In ADHD & Autism Kids ?
A). Speech difficulties in both ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are common but manifest differently due to the distinct nature of each condition.
In ADHD:
1. Speech difficulties often arise from core ADHD symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
2. Children with ADHD may have reduced auditory attention, making speech comprehension and production challenging.
3. Hyperactivity can lead to differences in tone, increased volume, rapid speech, mispronunciation, and disfluencies.
4. Impulsivity affects social communication skills, resulting in interrupting, talking excessively, difficulty taking turns, and challenges with understanding nonverbal cues.
5. These factors can result in speech clarity issues, organization of thoughts, and pragmatic language difficulties (e.g., staying on topic, conversational rules).
In Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD):
1. Speech difficulties often reflect neurological differences impacting social interaction, communication, and behavior.
2. Autistic individuals may experience problems initiating and sustaining conversations, using facial expressions, gestures, or intonation appropriately.
3. They may also display repetitive or fixated speech patterns, struggle with eye contact, and have difficulty with pragmatic aspects of language, such as turn-taking and understanding social cues.
4. Speech production might be affected by disrupted neural connectivity related to language areas, leading to articulation and reciprocal communication challenges.
5. When ADHD and autism co-occur, impulsivity from ADHD can exacerbate repetitive speech patterns typical of autism, complicating interactions further .
Therapeutic approaches for speech difficulties in both conditions often involve personalized speech therapy combined with behavioral and sensory integration strategies to improve communication effectiveness .
In sum, ADHD-related speech issues mainly stem from attention and impulsivity impacting speech clarity and social communication, while autism-related speech difficulties center around social communication impairments and atypical speech patterns. Coexisting ADHD and autism can compound these challenges.
1). స్పీచ్ థెరపీ అంటే ఏమిటి?
A) పిల్లల కోసం స్పీచ్ థెరపీ అనేది మాట్లాడే మరియు కమ్యూనికేషన్ సమస్యలను గుర్తించడం, అంచనా వేయడం, మరియు మెరుగుపరచడం కోసం రూపొందించబడిన ప్రత్యేక చికిత్స. ఇది పిల్లలు సమర్థవంతంగా మాట్లాడడం, అర్థం చేసుకోవడం మరియు సామాజికంగా కమ్యూనికేట్ చేయడం వంటి నైపుణ్యాలను అభివృద్ధి చేయడంలో సహాయపడుతుంది.
స్పీచ్ థెరపీ ఉచ్చారణలో ఇబ్బందులు (అర్టిక్యులేషన్), భాషను అర్థం చేసుకోవడం మరియు వ్యక్తీకరణలో సమస్యలు, తడబడటం (స్టటరింగ్) వంటి ప్రవాహ సమస్యలు, గొంతు సంబంధిత రుగ్మతలు మరియు మింగడంలో ఇబ్బందులు వంటి పలు అంశాలను పరిష్కరిస్తుంది.
1.1) పిల్లల్లో మొదటి మాటలు ఏమిటి?
A). సాధారణంగా పిల్లలు 10 నుండి 14 నెలల మధ్యలో తమ మొదటి మాటలు మాట్లాడటం ప్రారంభిస్తారు. వీటి లోపల ఎక్కువగా ఉపయోగించే మొదటి మాటలు పిల్లలు రోజువారీ జీవితంలో తరచుగా చూస్తూ, వింటూ ఉండే వ్యక్తులు లేదా వస్తువులకు సంబంధించినవే అవుతాయి. ఉదాహరణకు — “అమ్మ”, “నాన్న”, “బంతి”, “కుక్క”, “హాయ్”, “బై”, “వద్దు” వంటి మాటలు.
ఈ తొలి మాటలు సాధారణంగా పెదవులు కలపడం లేదా నాలుకను పై పళ్ల వెనుక ఉంచడం వంటి సులభమైన నోటి కదలికలతో ఏర్పడుతాయి (“అమ్మ”, “నాన్న” వంటి పదాలు). ఈ కదలికలు చిన్నారులకు సులభంగా చేయగలిగే వాటి కావడం వల్ల, తినే సమయంలో ఏర్పడే తొలిచూపు అనుభూతితో కూడా సంబంధం కలిగి ఉంటాయి.
సారాంశంగా చెప్పాలంటే — పిల్లల మొదటి మాటలు సాధారణం, భావోద్వేగపూరితం, మరియు సామాజిక సంబంధం ఉన్న పదాలు (“అమ్మ”, “నాన్న”, “హాయ్”, “బై”) రూపంలో ఒక సంవత్సరం వయసులోనే స్థిరంగా వాడడం ప్రారంభిస్తారు.
1.3) పిల్లల్లో మాట్లాడే (స్పీచ్) అభివృద్ధి మరియు దశలు ఏమిటి?
A). పిల్లల్లో మాట్లాడే నైపుణ్యం దశలవారీగా అభివృద్ధి చెందుతుంది. ప్రతి దశలో పిల్లలు శబ్దాలను గుర్తించడం, ఉచ్చరించడం, మరియు అర్థం చేసుకోవడం నేర్చుకుంటారు. క్రింది దశలు సాధారణంగా కనిపిస్తాయి:
➀ పుట్టినప్పటి నుండి 3 నెలల వరకు:
పిల్లలు శబ్దాలపై స్పందించడం ప్రారంభిస్తారు. అమ్మ, నాన్న వాయిస్ వినగానే నవ్వడం లేదా మెలకువగా చూడడం మొదలుపెడతారు. కూతలు (“కూ”, “ఆ”) వంటి శబ్దాలు చేస్తారు.
➁ 4 నుండి 6 నెలల వరకు:
పిల్లలు కొత్త శబ్దాలతో ఆడుకోవడం ప్రారంభిస్తారు. “బా”, “మా”, “పా” వంటి శబ్దాలు చెబుతారు. ఆ శబ్దాలు పునరావృతమవుతాయి (“బాబా”, “మామా”).
➂ 7 నుండి 12 నెలల వరకు:
పిల్లలు తమ చుట్టూ ఉన్నవారి మాటలను అనుకరించడానికి ప్రయత్నిస్తారు. “అమ్మ”, “నాన్న”, “బై”, “హాయ్” వంటి సరళమైన పదాలు వాడటం ప్రారంభిస్తారు. కొన్ని సులభమైన ఆదేశాలను అర్థం చేసుకోవడం మొదలుపెడతారు.
➃ 1 నుండి 2 సంవత్సరాల వరకు:
పద భాండారం వేగంగా పెరుగుతుంది. “బంతి ఇవ్వు”, “అమ్మ రా” వంటి రెండు పదాల వాక్యాలు వాడడం ప్రారంభిస్తారు.
➄ 2 నుండి 3 సంవత్సరాల వరకు:
వాక్యాలు మరింత పొడవుగా మారతాయి. చిన్న ప్రశ్నలు అడగడం, కథలు వినడం ఇష్టపడతారు. సుమారు 200–500 పదాలు మాట్లాడగలుగుతారు.
➅ 3 నుండి 5 సంవత్సరాల వరకు:
పిల్లలు వ్యాకరణపరంగా సరైన వాక్యాలు ఉపయోగిస్తారు. ఆలోచనలు, భావాలు స్పష్టంగా చెప్పగలుగుతారు. ఇతరులతో సులభంగా సంభాషణ కొనసాగించగలుగుతారు.
2. స్పీచ్ డిలే అంటే ఏమిటి?
A). పిల్లల్లో స్పీచ్ డిలే అనేది ఒక పరిస్థితి, ఇందులో పిల్లలు తమ వయస్సుకు తగినంత వేగంగా మాట్లాడే మరియు భాషా నైపుణ్యాలను అభివృద్ధి చేసుకోలేరు.
“స్పీచ్” అంటే శబ్దాలు మరియు పదాలను ఉత్పత్తి చేసే శారీరక చర్య,
“లాంగ్వేజ్” అంటే ఆ పదాలను అర్థం చేసుకొని ఇతరులతో కమ్యూనికేట్ చేయడం.
స్పీచ్ డిలే ఉన్న పిల్లలు కొన్ని పదాలు లేదా వాక్యాలు ఉపయోగించవచ్చు కానీ అవి ఇతరులకు అర్థమయ్యే విధంగా స్పష్టంగా ఉండకపోవచ్చు లేదా సరైన శబ్దాలను తయారు చేయడంలో కష్టపడవచ్చు.
ఈ ఆలస్యం ఉచ్చారణ (articulation) సమస్యలు, నోటితో సంబంధించిన కదలికల నియంత్రణ (oral-motor skills – పెదవులు, నాలుక, దవడ సమన్వయం), లేదా భాషను అర్థం చేసుకోవడం మరియు వ్యక్తపరచడంలో ఇబ్బందులు వంటి కారణాల వల్ల రావచ్చు.
స్పీచ్ డిలేకు ప్రధాన కారణాలు:
నోటి భాగాల్లో నిర్మాణ లోపాలు,
వినికిడి సమస్యలు,
మెదడులో మాట్లాడే కండరాలపై ప్రభావం చూపే ప్రాంతాల్లో లోపాలు,
ఆటిజం వంటి అభివృద్ధి సంబంధిత రుగ్మతలు,
కొన్నిసార్లు స్పష్టమైన కారణం గుర్తించబడకపోవడం.
2. స్పీచ్ డిలే అంటే ఏమిటి?
A). పిల్లల్లో స్పీచ్ డిలే అనేది ఒక పరిస్థితి, ఇందులో పిల్లలు తమ వయస్సుకు తగినంత వేగంగా మాట్లాడే మరియు భాషా నైపుణ్యాలను అభివృద్ధి చేసుకోలేరు.
“స్పీచ్” అంటే శబ్దాలు మరియు పదాలను ఉత్పత్తి చేసే శారీరక చర్య,
“లాంగ్వేజ్” అంటే ఆ పదాలను అర్థం చేసుకొని ఇతరులతో కమ్యూనికేట్ చేయడం.
స్పీచ్ డిలే ఉన్న పిల్లలు కొన్ని పదాలు లేదా వాక్యాలు ఉపయోగించవచ్చు కానీ అవి ఇతరులకు అర్థమయ్యే విధంగా స్పష్టంగా ఉండకపోవచ్చు లేదా సరైన శబ్దాలను తయారు చేయడంలో కష్టపడవచ్చు.
ఈ ఆలస్యం ఉచ్చారణ (articulation) సమస్యలు, నోటితో సంబంధించిన కదలికల నియంత్రణ (oral-motor skills – పెదవులు, నాలుక, దవడ సమన్వయం), లేదా భాషను అర్థం చేసుకోవడం మరియు వ్యక్తపరచడంలో ఇబ్బందులు వంటి కారణాల వల్ల రావచ్చు.
స్పీచ్ డిలేకు ప్రధాన కారణాలు:
నోటి భాగాల్లో నిర్మాణ లోపాలు,
వినికిడి సమస్యలు,
మెదడులో మాట్లాడే కండరాలపై ప్రభావం చూపే ప్రాంతాల్లో లోపాలు,
ఆటిజం వంటి అభివృద్ధి సంబంధిత రుగ్మతలు,
కొన్నిసార్లు స్పష్టమైన కారణం గుర్తించబడకపోవడం.
3. స్పీచ్ మైల్స్టోన్స్ అంటే ఏమిటి?
A). స్పీచ్ మైల్స్టోన్స్ అంటే పిల్లలు పెరుగుతున్న కొద్దీ మాట్లాడటం మరియు భాషను అర్థం చేసుకోవడంలో సాధించే సాధారణ అభివృద్ధి దశలు మరియు నైపుణ్యాలు. ఈ మైల్స్టోన్స్ ద్వారా పిల్లల భాషా అభివృద్ధి వయస్సుకు తగ్గ రీతిలో జరుగుతోందా లేదా ఆలస్యం ఉందా అనే విషయం తెలుసుకోవచ్చు.
స్పీచ్ మైల్స్టోన్స్లో శబ్దాలను గుర్తించడం, మొదటి మాటలు పలకడం, సరళమైన వాక్యాలు రూపొందించడం, మరియు ఇతరులతో సంభాషణ చేయడం వంటి అంశాలు ఉంటాయి. సాధారణంగా ఇవి పుట్టినప్పటి నుండి ఐదేళ్ల వయస్సు వరకు దశలవారీగా అభివృద్ధి చెందుతాయి.
క్రింద వయస్సు ప్రాతిపదికగా సాధారణ స్పీచ్ మైల్స్టోన్స్ ఇవ్వబడ్డాయి 👇
వయస్సు పరిధి ముఖ్య మైల్స్టోన్స్ (మాటల అభివృద్ధి లక్షణాలు)
పుట్టినప్పటి నుండి 3 నెలల వరకు అమ్మా, నాన్నా వాయిస్లు గుర్తించడం, వేర్వేరు రకాల ఏడుపు ద్వారా అవసరాలు వ్యక్తం చేయడం, “కూ” వంటి శబ్దాలు చేయడం
4 నుండి 6 నెలల వరకు శబ్దాలకు మరియు టోన్ మార్పులకు స్పందించడం, “బా”, “మా”, “పా” వంటి బాబ్లింగ్ శబ్దాలు పలకడం
7 నుండి 11 నెలల వరకు పేరు పిలిచినప్పుడు స్పందించడం, హావభావాలు (చేతులతో చూపించడం, బై చెప్పడం) ఉపయోగించడం, పరిచయమైన పదాలు గుర్తించడం
12 నుండి 24 నెలల వరకు మొదటి మాటలు పలకడం (“అమ్మ”, “నాన్న”), సులభమైన ఆదేశాలను అర్థం చేసుకోవడం (“రా”, “ఇవ్వు”), రెండు పదాలను కలిపి మాట్లాడడం (“అమ్మ రా”)
2 నుండి 3 సంవత్సరాల వరకు సరళమైన వాక్యాలు మాట్లాడడం, రెండు దశల ఆదేశాలను పాటించడం, వస్తువుల పేర్లు చెప్పడం
3 నుండి 4 సంవత్సరాల వరకు వందలాది పదాలను ఉపయోగించడం, వస్తువులను వివరిస్తూ మాట్లాడడం, ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు ఇవ్వడం
4 నుండి 5 సంవత్సరాల వరకు క్లిష్టమైన ప్రశ్నలను అర్థం చేసుకోవడం, పొడవైన వాక్యాలు మాట్లాడడం, చిన్న కథలు చెప్పడం
4) స్పీచ్ థెరపీ లో ఉపయోగించే పరికరాలు ?
A). స్పీచ్ థెరపీ అనేది భాష, మాట్లాడటం, ఆర్టిక్యులేషన్, నోటీ కదలికలు, ఫ్లూయెన్సీ మరియు నోటీ మూతి కదలికలను మెరుగుపరచడానికి ప్రత్యేక పరికరాలు ఉపయోగిస్తుంది. ఇక్కడ కొన్ని సాధారణ మరియు సమర్థవంతమైన పరికరాలు ఉన్నాయి:
—
ఆర్టిక్యులేషన్ మరియు నోటీ మోటార్ స్కిల్స్ కోసం ప్రత్యేక పరికరాలు
Speech Buddies: “l,” “r,” “s,” “sh,” “ch” వంటి ధ్వనులను సరిగా ఉత్పత్తి చేయడానికి జిభను సరిగా ఉంచే పరికరం.
Talktools Bilabial Shapes: “m,” “p,” “b” వంటి బిలాబియల్ ధ్వనులను అభ్యసించడానికి రంగు మరియు స్పర్శ ఫీడ్బ్యాక్ తో ఉపయోగించే పరికరం.
Talktools Tactile Tubes: లిప్ రౌండింగ్ ద్వారా వౌల్ ఉత్పత్తిని మెరుగుపరచడానికి మరియు స్పర్శ ఫీడ్బ్యాక్ అందించడానికి.
Talktools Apraxia Blocks: రంగు కోడ్ బ్లాక్స్, జా స్థిరత్వాన్ని పెంచి వౌల్ ధ్వనుల కోసం సహాయపడతాయి, ముఖ్యంగా అప్రాక్సియా కోసం.
Talktools Horn and Straw Kits: శ్వాస నియంత్రణ, లిప్, జిభ మరియు జా కదలికలను మెరుగుపరచడానికి ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
Chewy Tubes: నోటీ సెన్సరీ ఉద్దీపన మరియు జా మసిల్స్ బలపరచడానికి.
Tongue Tip Elevation/Lateralization Tools: “t,” “d,” “n,” “l” వంటి ధ్వనులకు జిభ కదలికలు అభ్యసించడానికి.
Tongue Depressors: జా స్థిరత్వం మరియు లిప్ మూత వ్యాయామాల కోసం.
Nose Flute: నాసల్ ధ్వనులను అభ్యసించడానికి మరియు నాసల్ ఎయిర్ ఫ్లోను ప్రేరేపించడానికి.
—
సాధారణ థెరపీ సహాయ పరికరాలు మరియు టెక్నాలజీ
మిర్రర్స్ (అద్దాలు): రోగి తన నోటీ మరియు జిభ కదలికలను చూసి ధ్వని సరైనదో తనిఖీ చేసుకోవడానికి.
పిక్చర్ కార్డ్స్ & విజువల్ ఎడ్స్: పదాలు మరియు ధ్వనులను విజువల్ అసోసియేషన్ ద్వారా అభ్యసించడానికి.
అడాప్టివ్ కమ్యూనికేషన్ స్విచ్లు: నాన్-వerbల్ రోగుల కమ్యూనికేషన్ కోసం ఉపయోగించే పరికరాలు.
5) స్పీచ్ థెరపీ లో ఉపయోగించే సాంకేతికతలు (Techniques) ?
A). స్పీచ్ మరియు కమ్యూనికేషన్ సమస్యలను పరిష్కరించడానికి వివిధ రకాల స్పీచ్ థెరపీ విధానాలు ఉన్నాయి. ప్రతి విధానం వ్యక్తిగత సమస్యలకు అనుగుణంగా ఉంటుంది. ప్రధాన విధానాలు:
—
1. ఆర్టిక్యులేషన్ థెరపీ (Articulation Therapy)
మాటల ధ్వనులను స్పష్టంగా మరియు ఖచ్చితంగా ఉత్పత్తి చేయడం కోసం అభ్యసించడం.
నోటీ, జిభ, జా కదలికలను సమన్వయ పరచి సరైన ఉచ్చారణ సాధించడం.
2. భాషా (లాంగ్వేజ్) థెరపీ (Language Therapy)
భాషా అవగాహన, పదజాలం, వ్యాకరణం, అర్థం, వ్యక్తీకరణను మెరుగుపరచడం.
స్టోరీటెల్లింగ్, నిర్మాణబద్ధమైన వ్యాయామాలు వంటి కార్యకలాపాల ద్వారా అభ్యసించడం.
3. ఫ్లూయెన్సీ థెరపీ (Fluency Therapy)
స్టటరింగ్ లేదా మాటలో విరామం ఉన్న వ్యక్తులకు సహాయం.
శ్వాస వ్యాయామాలు, రిలాక్సేషన్, మాట మార్పు సాంకేతికతలతో మాటను సాఫీగా చేయడం.
4. వాయిస్ థెరపీ (Voice Therapy)
స్వరం, పిచ్, వాల్యూమ్, రిజనెన్స్ సమస్యలను పరిష్కరించడం.
స్వర కండరాలను బలపరచడం, ఆరోగ్యకరమైన వాయిస్ అలవాట్లను అభ్యసించడం.
5. ఓరల్ మోటార్ థెరపీ (Oral Motor Therapy)
మాట్లాడటానికి మరియు మింగడానికి అవసరమైన నోటీ కండరాలను బలపరచడం.
ఊపడం, తోతడం, నొక్కడం వంటి వ్యాయామాలు.
6. ఆగ్మెంటేటివ్ & అల్టర్నేటివ్ కమ్యూనికేషన్ (AAC)
తీవ్ర స్పీచ్ సమస్యలున్న వ్యక్తుల కోసం పిక్చర్ ఎక్స్చేంజ్ కమ్యూనికేషన్ వంటి పరికరాలు మరియు వ్యూహాలు ఉపయోగించడం.
7. ప్రత్యేక సాంకేతికతలు (Specialized Methods)
VitalStim Therapy: మింగే సమస్యలకు విద్యుత్ ఉత్ప్రేరక (Electrical Stimulation) ఉపయోగించడం.
Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT): మాట వాల్యూమ్ మెరుగుపరచడం.
Cognitive-Communication Therapy: పెద్దలు, మస్తిష్క గాయాలు లేదా degenerative పరిస్థితులు ఉన్న వారికి.
6) ఆటిజం ఉన్న పిల్లలకు ఉపయోగించే స్పీచ్ టూల్స్ (Speech Tools for Autism Kids)
స్పీచ్ టూల్స్ అంటే ఏమిటి?
A). స్పీచ్ థెరపీ లో ఉపయోగించే ప్రత్యేక పరికరాలు, వ్యక్తి కమ్యూనికేషన్ నైపుణ్యాలను మెరుగుపరచడానికి ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
ఇవి టాక్టైల్ (స్పర్శ), విజువల్ (దృష్టి), ఆడిటరీ (శ్రవణ) సూచనలు అందించగా, జిభ, నోటీ, జా కదలికలను మార్గనిర్దేశం చేస్తాయి.
ఇవి సాంప్రదాయ స్పీచ్ థెరపీ కంటే ముందుగా, బహుళ ఇంద్రియాలను ఉపయోగించి, నేర్చుకోవడం సులభం మరియు వేగవంతం చేస్తాయి.
ఆటిజం కోసం స్పీచ్ టూల్స్ మరియు థెరపీ లక్ష్యం:
ఆటిజం ఉన్న వ్యక్తుల వర్బల్, నాన్-వర్బల్, మరియు సోషల్ కమ్యూనికేషన్ స్కిల్స్ ను మెరుగుపరచడం.
వ్యక్తిగత అవసరాలకు అనుగుణంగా టూల్స్ మరియు థెరపీ ప్లాన్ రూపొందించడం.
—
స్పీచ్ టూల్స్ మరియు వాటి ఉపయోగాలు
1. Speech Buddies:
జిభ స్థానం మార్గనిర్దేశం చేస్తూ “l”, “r”, “s”, “sh”, “ch” వంటి ధ్వనులను అభ్యసించడంలో సహాయపడతాయి.
2. Talktools:
వివిధ పరికరాలు, ప్రత్యేక ధ్వనుల కోసం సహాయం చేస్తాయి:
Bilabial Shapes: “m”, “p”, “b” వంటి బిలాబియల్ ధ్వనులకు సహాయం.
Tactile Tubes: లిప్ రౌండింగ్ మరియు వౌల్ ఉత్పత్తికి సహాయపడతాయి, ముఖ్యంగా అప్రాక్సియా లేదా బలహీన కండరాల కోసం.
Apraxia Blocks: జా స్థిరత్వం కోసం, వౌల్ ధ్వనులు మెరుగుపరచడం.
Tongue Tip Elevation/Lateralization Tool: “t”, “d”, “n”, “l” వంటి ధ్వనుల కోసం జిభ కదలికలు సరిగ్గా చేయడంలో సహాయం.
3. Talktools Horn Kit:
స్పీచ్ ఫ్లూయెన్సీ కోసం అవసరమైన శ్వాస నియంత్రణను మెరుగుపరుస్తుంది.
4. Chewy Tubes:
జా కండరాలను బలపరచడం మరియు నోటీ సెన్సరీ స్కిల్స్ మెరుగుపరచడం.
5. Nose Flute:
“m” మరియు “n” వంటి నాసల్ ధ్వనుల కోసం నాసల్ ఎయిర్ ఫ్లో శిక్షణ.
6. AAC (Augmentative & Alternative Communication) పరికరాలు:
నాన్-వర్బల్ ఆటిజం పిల్లల కమ్యూనికేషన్ కోసం టెక్నాలజీ మరియు యాప్స్ ఉపయోగించడం.
7. విజువల్ సపోర్ట్స్ (Visual Supports):
పిక్చర్ ఎక్స్చేంజ్ కార్డ్స్, స్టోరిబోర్డ్స్ ద్వారా అర్థం చేసుకోవడం మరియు వ్యక్తీకరణలో సహాయం.
8. ప్లే-బేస్డ్ టెక్నిక్స్ (Play-based Techniques):
ఇంటరాక్టివ్ ప్లే ద్వారా సోషల్ కమ్యూనికేషన్ స్కిల్స్ అభ్యసించడం.
7) ఆటిజం లో ఆర్టిక్యులేషన్ స్పీచ్ థెరపీ అంటే ఏమిటి?
A). ఆర్టిక్యులేషన్ థెరపీ (Articulation Therapy) అనేది ఆటిజం ఉన్న పిల్లల కోసం ప్రత్యేకమైన వైద్యపద్ధతి, ఇది పిల్లల స్పీచ్ స్పష్టతను (speech intelligibility) మెరుగుపరచడం లక్ష్యంగా రూపొందించబడింది.
ఇది ఒక పద్ధతిగా ప్రత్యేక ధ్వనులను (target sounds) సరైనంగా ఉత్పత్తి చేయడానికి ప్రాక్టీస్ చేయించటం.
ప్రారంభం ఒక ధ్వనితో (isolation) మొదలై, తరువాత సిల్లబుల్స్ (syllables), పదాలు, వాక్యాలు, కథలు, సంభాషణ దాకా అభ్యసనం చేస్తారు.
దీని ద్వారా స్పష్టమైన స్పీచ్ ప్రతి సందర్భంలో (generalization across contexts) సాధ్యమవుతుంది.
—
పద్ధతులు మరియు సాంకేతికతలు
వాయిస్ ఇమిటేషన్ (Vocal imitation): పిల్లలు శ్రవణం ద్వారా ధ్వనిని పునరావృతం చేస్తారు.
ప్రాంప్టింగ్ (Prompting) & షేపింగ్ (Shaping): ధ్వనులను సరిగా ఉత్పత్తి చేయడానికి సూచనలు మరియు మార్గనిర్దేశం.
ఫిజికల్ క్యూస్ (Physical cues): జిభ, నోటీ మరియు లిప్ స్థానాన్ని సరిచేయడం.
ఇంటరాక్టివ్ పద్ధతులు: ఆటలు, యాప్స్, పిల్లల ఇష్టాలకు అనుగుణమైన ఫన్ వ్యాయామాలు.
—
ఆర్టిక్యులేషన్ సమస్యలు ఎందుకు ఉంటాయి?
ఆటిజం ఉన్న పిల్లలకు స్పీచ్ సౌండ్ లేదా నోటీ-మోటార్ సమస్యలు ఉంటాయి.
వారు కష్టపడే ధ్వనులను పరిష్కరించడానికి లెర్నింగ్ ప్రాసెస్ను చిన్న దశలలో విభజించి, వారి ప్రత్యేక లెర్నింగ్ స్టైల్కు అనుగుణంగా పద్ధతులు ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
స్పీచ్ అర్ధం కాకపోవడం వల్ల కమ్యూనికేషన్ మరియు సోషల్ ఇంటరాక్షన్ ప్రభావితమవుతుంది.
—
ఆర్టిక్యులేషన్ థెరపీ ముఖ్య భాగాలు
1. ధ్వనుల isolation (ప్రత్యేకంగా ధ్వనిని అభ్యసించడం)
2. సిల్లబుల్స్ మరియు పదాల్లో ధ్వనులను అభ్యసించడం
3. లక్ష్య ధ్వనులతో వాక్యాలు నిర్మించడం
4. కథలు చెబుతూ ధ్వనులను ఉపయోగించడం
5. సంభాషణల ద్వారా ప్రాక్టీస్ (skill generalization)
8) ఆటిజం లో పునరావృతమైన మాట (Repetitive Speech) తగ్గించడానికి ఎలా?
A). ఆటిజం ఉన్న పిల్లలలో, ముఖ్యంగా ఎకొలాలియా (echolalia) కు, పునరావృతమైన మాట తగ్గించడానికి సమర్థవంతమైన మార్గాలు:
స్పీచ్ థెరపీ, బిహేవియరల్ ఇన్టర్వెన్షన్స్, మరియు సహాయక పరికరాలు ఉపయోగించడం.
—
స్పీచ్ థెరపీ పద్ధతులు
Delayed echoing: చిన్న వాయిదాతో పునరావృతం చేస్తూ, అర్థవంతమైన మాటకు మార్గనిర్దేశం.
Expansion of phrases: చిన్న పదాలను విస్తరిస్తూ, పూర్తి వాక్యాలుగా మార్చడం.
Mitigation: పునరావృతం కంటే అర్థవంతమైన కమ్యూనికేషన్ ను ప్రోత్సహించడం.
—
బిహేవియరల్ పద్ధతులు
Visual supports: చిత్రాలు, షెడ్యూల్స్ ద్వారా అర్థం చేసుకోవడం సులభం.
Role-playing: పాత్రల ద్వారా మాటల వాడకం అభ్యసించడం.
Positive reinforcement: స్వతంత్ర మాట్లాడటానికి ప్రోత్సాహం.
—
ప్రత్యేక పద్ధతులు
1. Response Interruption and Redirection (RIR):
పునరావృతమైన మాటను అడ్డుకోవడం.
వ్యక్తి దృష్టిని వేరే activity లేదా ప్రశ్నకు మార్చడం.
Visual schedules మరియు structured choice questions ద్వారా ఆందోళన తగ్గించి, స్పష్టమైన అంచనాలు ఇవ్వడం.
2. Early & intensive intervention:
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) మరియు Verbal Behavior Therapy వాడడం.
ఫంక్షనల్ కమ్యూనికేషన్ బలపరచడం, పునరావృతమైన పదాలను తగ్గించడం.
9) ఆటిజంలో ఎకోలేలియా (Echolalia) స్పీచ్ అంటే ఏమిటి?
** నిర్వచనం:**
ఎకోలేలియా అనేది ఆటిజం ఉన్న వ్యక్తుల్లో కనిపించే ఒక మాట మళ్ళీ మళ్ళీ చెప్పే నమూనా, ఇందులో వారు వినిన పదాలు, వాక్యాలు లేదా శబ్దాలను పునరావృతం చేస్తారు. ఇది తక్షణం లోనైనా లేదా కొంత సమయం తర్వాత కూడా జరుగుతుంది.
** ఉద్దేశ్యాలు మరియు ఉపయోగాలు:**
మళ్ళీ మళ్ళీ పదాలు చెప్పడం వ్యర్థంగా కనిపించవచ్చు, కానీ ఇది ఆటిజం ఉన్న వ్యక్తుల కోసం కొన్ని ముఖ్యమైన విధులు కలిగి ఉంటుంది:
భాషా అభివృద్ధి: పదాలు, వాక్యాలు మరియు వాక్య నిర్మాణాలను ప్రాక్టీస్ చేయడం.
సామాజిక సంబంధాలు: ఇతరులతో కమ్యూనికేట్ చేయడానికి, కనెక్ట్ అయ్యేందుకు.
భావన వ్యక్తీకరణ: భావాలను లేదా స్పందనలను చూపించడం.
స్వీయ నియంత్రణ: ఆత్మశాంతి, ఒత్తిడి తగ్గించడం, లేదా స్వీయ ఉద్దీపన (self-stimulation).
** ఎకోలేలియా రకాలూ:**
1. తక్షణ ఎకోలేలియా (Immediate Echolalia): పదాలు లేదా వాక్యాలను తక్షణం విన్న వెంటనే పునరావృతం చేయడం.
2. విలంబిత ఎకోలేలియా (Delayed Echolalia): పదాలు లేదా వాక్యాలను కొంత సమయం తర్వాత పునరావృతం చేయడం, కొన్ని రోజుల లేదా నెలల తర్వాత కూడా కావచ్చు.
10) ఎకోలేలియా (Echolalia) కేవలం ఆటిజం పిల్లలలోనే సంభవించగలదా లేదా ADHD పిల్లలలో కూడా వస్తుందా?
A). ఎకోలేలియా అనేది ఇతరుల మాటలు లేదా వాక్యాలను పునరావృతం చేయడం. ఇది ఆటిజం స్పెక్ట్రమ్ డిసార్డర్ (ASD) లో ఎక్కువగా కనిపిస్తుందు, కానీ కొంతమంది ADHD ఉన్న వ్యక్తులలో కూడా ఏర్పడవచ్చు.
ADHD లో: ఎకోలేలియా ADHD యొక్క ప్రధాన లక్షణం కాదు. ADHD లో ఎకోలేలియా మనోనైపుణ్యం (impulsivity), దృష్టి సమస్యలు, లేదా ఇతర న్యూరోడెవలప్మెంటల్ పరిస్థితులు కారణంగా కొన్నిసార్లు కనిపించవచ్చు.
Autism లో: ఎకోలేలియా చాలా సాధారణం, ASD ఉన్న వ్యక్తుల సుమారుగా 75–80% కి అభివృద్ధి సమయంలో ఎకోలేలియా కనిపిస్తుంది. ఇది సొంత భాషను రూపొందించలేనప్పుడు కమ్యూనికేషన్ కై ఒక మార్గంగా ఉపయోగపడుతుంది.
Autism లో ఎకోలేలియా:
1. ASD లో ఎకోలేలియా అత్యంత సాధారణం మరియు కీ లక్షణంగా పరిగణించబడుతుంది.
2. ఆటిజం ఉన్న పిల్లలు సాధారణంగా దీన్ని ఎక్కువసేపు మరియు ఎక్కువగా ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
ADHD లో ఎకోలేలియా:
1. ADHD లో ఇది ప్రధాన లక్షణం కాదు, కానీ కొందరికి అసహనం, దృష్టి లోపాలు, లేదా సెన్సరీ ప్రాసెసింగ్ సమస్యలు కారణంగా కనిపించవచ్చు.
2. ADHD లో భాషా లేదా కమ్యూనికేషన్ సమస్యలు ప్రధానం కాదు, కాబట్టి ఎకోలేలియా ఎక్కువగా ASD వంటి మరో న్యూరోడెవలప్మెంటల్ పరిస్థితితో కలిసినప్పుడు కనిపిస్తుంది.
3. సుమారుగా 50–70% ASD ఉన్నవారికి ADHD కూడా ఉండవచ్చు, కాబట్టి లక్షణాల్లో కొంత అవలంబన (overlap) ఉంటుంది.
11) స్పీచ్లో స్టామ్మరింగ్ / స్టట్టరింగ్ అంటే ఏమిటి?
వ్యాఖ్య:
స్టామ్మరింగ్ లేదా స్టట్టరింగ్ అనేది మాటల్ని సహజంగా పలకడంలో అడ్డంకులు ఏర్పడడం, పదాల పునరావృతం, పొడిగింపు, లేదా బ్లాక్స్ (మాట చెబుతుండగా ఆగిపోవడం) వంటి లక్షణాలతో కనిపించే స్పీచ్ సమస్య. ఇది వయసు, కారణాలు, లక్షణాలు, మరియు చికిత్సా విధానాల ప్రకారం మూడు రకాలుగా వర్గీకరించబడుతుంది:
—
1. Developmental Stuttering (అభివృద్ధి సంబంధిత స్టట్టరింగ్)
ఎప్పుడు వస్తుంది: చిన్నపిల్లల్లో (2–5 ఏళ్ళ వయసులో)
కారణం: సాధారణ భాషా అభివృద్ధికి సంబంధించిన కారణాలు
లక్షణాలు: పదాల పునరావృతం, పొడిగింపు, బ్లాక్స్; మాట్లాడే సందర్భాలపై ఆధారపడి మారుతూ ఉంటాయి
గమనిక: ఎక్కువమంది పిల్లల్లో ఇది కాలానుగుణంగా తగ్గిపోవచ్చు, లేదా థెరపీతో మెరుగవుతుంది. ఆందోళన (anxiety) ఎక్కువైతే సమస్య పెరుగుతుంది
చికిత్స: స్పీచ్ థెరపీ మరియు కుటుంబ మద్దతు
—
2. Neurogenic Stuttering (న్యూరోజెనిక్ స్టట్టరింగ్)
ఎప్పుడు వస్తుంది: మస్తిష్కం గాయాలు, స్ట్రోక్, లేదా ఇతర న్యూరోలోజికల్ సమస్యల తరువాత ఏ వయసులోనైనా
కారణం: మస్తిష్కంలోని స్పీచ్ నియంత్రణ క్షేత్రాలకు సంబంధించిన న్యూరోలోజికల్ సమస్యలు
లక్షణాలు: అన్ని మాట్లాడే సందర్భాల్లోనూ స్థిరమైన డిస్ఫ్లువెన్సీలు; ఇతర న్యూరోలోజికల్ లక్షణాలు కూడా ఉండవచ్చు
చికిత్స: స్పీచ్ మోటార్ రీప్రోగ్రామింగ్, ఫ్లూయెన్సీ షేపింగ్, రీహాబిలిటేషన్
—
3. Psychogenic Stuttering (సైకాలజికల్ / మానసిక కారణాల స్టట్టరింగ్)
ఎప్పుడు వస్తుంది: మానసిక ట్రామా, స్ట్రెస్, లేదా మానసిక ఆరోగ్య సమస్యల కారణంగా
కారణం: న్యూరోలోజికల్ గాయాలు కాకుండా మానసిక సమస్యలు
లక్షణాలు: ఆకస్మికంగా వస్తుంది; స్ట్రెస్ లేదా భావోద్వేగ పరిస్థితులపై ఆధారపడి మారుతూ ఉంటుంది; affected individuals కొద్దిగా మాత్రమే ఆందోళన చూపిస్తారు (“la belle indifference”)
చికిత్స: సైకోథెరపీ, కాగ్నిటివ్ బిహేవియర్ థెరపీ (CBT), మరియు మద్దతుగా స్పీచ్ థెరపీ
12) మోటార్ స్పీచ్ డిసార్డర్ (Motor Speech Disorder) అంటే ఏమిటి?
వ్యాఖ్య:
మోటార్ స్పీచ్ డిసార్డర్ అనేది న్యూరోలోజికల్ సమస్య, ఇది వ్యక్తి మాటలు పలికే ప్రణాళిక, ప్రోగ్రామింగ్, నియంత్రణ, సమన్వయం మరియు అమలు సామర్థ్యాన్ని ప్రభావితం చేస్తుంది. సాధారణంగా ఇది నర్వస్ సిస్టమ్ లో లోపం లేదా గాయాల వల్ల వస్తుంది.
ఈ డిసార్డర్లు శరీరానికి సహజంగా మాట్లాడే సామర్థ్యాన్ని భంగం చేస్తాయి, ఎక్కువగా సెంట్రల్ లేదా పెరిఫెరల్ నర్వస్ సిస్టమ్ లో నష్టం లేదా డిస్ఫంక్షన్ కారణంగా.
—
మోటార్ స్పీచ్ డిసార్డర్స్ రకాలు:
1. Dysarthria (డిసార్ట్రియా)
లక్షణాలు: మాటలు మెల్లగా, అస్పష్టంగా, తప్పుడు శబ్దాలతో వస్తాయి
కారణం: స్పీచ్ కోసం ఉపయోగించే మొకటిన్నటి కండరాలు (జిభ, ఒత్తిపోటు, వాయిస్ బాక్స్) బలహీనత లేదా అసమన్వయం కారణంగా
ఉత్పత్తి: సెంట్రల్ న్యూరాలజికల్ నష్టం, స్ట్రోక్, తల గాయం, లేదా degenerative diseases
2. Apraxia of Speech (అప్రాక్సియా ఆఫ్ స్పీచ్)
లక్షణాలు: కండర బలహీనత లేకపోయినా, మాటలు పలికే కదలికలను ప్రణాళిక చేయడంలో మరియు క్రమపరచడంలో కష్టాలు
రకాలు:
Childhood Apraxia: జన్మతే వచ్చే (congenital)
Acquired Apraxia: స్ట్రోక్ వంటి న్యూరాలజికల్ గాయాల తర్వాత
సమస్యలు: మెల్లని మాటలు, అసమాన శబ్ద తప్పులు
13) పిల్లల్లో స్పీచ్ డిసార్డర్స్ రకాలు (Types of Speech Disorders in Children)
స్పీచ్ డిసార్డర్స్ అనేది పిల్లలు సరైన శబ్దాలు ఉత్పత్తి చేయలేకపోవడం, మాట్లాడడంలో సజావుగా ఉండకపోవడం, లేదా వారి వాయిస్ ను సరిగ్గా ఉపయోగించలేకపోవడం వంటి సమస్యలను సూచిస్తుంది.
—
Speech Disorders రకాలు:
1. Apraxia of Speech (అప్రాక్సియా ఆఫ్ స్పీచ్)
మాటలు పలికే కదలికలను సమన్వయపరచడంలో కష్టం
సాధారణంగా న్యూరాలజికల్ సమస్యల వల్ల వస్తుంది
2. Dysarthria (డిసార్ట్రియా)
స్పీచ్ కండరాల బలహీనత లేదా పారాలిసిస్
మాటలు మెల్లగా లేదా అస్పష్టంగా వస్తాయి
3. Stuttering / Stammering (స్టట్టరింగ్ / స్టామ్మరింగ్)
మాటల్లో పునరావృతం, పొడిగింపు, బ్లాక్స్ వంటి అంతరాయం
4. Speech Sound Disorders (శబ్ద ఉత్పత్తి సమస్యలు)
Articulation Disorders: శబ్దాలను శారీరకంగా ఉత్పత్తి చేయడంలో కష్టం
Phonemic Disorders: శబ్దాల మధ్య తేడాలను అర్థం చేసుకోవడంలో కష్టం
5. Voice Disorders (వాయిస్ డిసార్డర్స్)
వాయిస్ కార్డ్స్ లేదా లారింక్స్ సమస్యల కారణంగా గొంత గొంతుగా, ఊపిరితీతతో, లేదా మాట్లాడలేకపోవడం
6. Aphasia (అఫాసియా)
భాషా సమస్య, స్పీచ్ అర్థం చేసుకోవడం లేదా వ్యక్తీకరించడంలో కష్టం
7. Cluttering (క్లట్టరింగ్)
వేగంగా మరియు అసమానంగా మాట్లాడడం, అర్థం చేసుకోవడం కష్టం
8. Lisps (లిస్ప్స్)
/s/ మరియు /z/ వంటి సిలబెంట్ శబ్దాలను తప్పుగా పలకడం
9. Muteness (నిశ్శబ్దం / మ్యూట్నెస్)
మొత్తం మాటలు పలకలేకపోవడం
14) స్పీచ్ లో పాల్గొనే Activities (Speech Activities in Children)
స్పీచ్ సంబంధించిన Activities అనేవి వెర్బల్ మరియు నాన్వెర్బల్ కమ్యూనికేషన్ స్కిల్స్ ను మెరుగుపరచడానికి రూపొందించబడిన ఇంటరాక్టివ్ మరియు ప్రాక్టికల్ ఎక్సర్సైజ్లు. ఇవి క్లారిటీ, వాక్యసంపద, లిసనింగ్, వ్యక్తీకరణ, మరియు మాట్లాడే విశ్వాసాన్ని పెంచడం లక్ష్యం.
—
స్పీచ్ Activities రకాలు:
1. Impromptu Speaking (తక్షణం మాట్లాడటం)
ఇవ్వబడిన టాపిక్ పై వెంటనే మాట్లాడటం
ఫాస్ట్ థింకింగ్ మరియు క్లియర్ ఎక్స్ప్రెషన్ అభ్యాసం
2. Storytelling / Continuous Story (కథ చెప్పడం / కొనసాగించడం)
కథను సృష్టించడం లేదా కొనసాగించడం
క్రియేటివిటీ మరియు నారేటివ్ స్కిల్స్ పెంపొందిస్తుంది
3. Debates (వాదసమర్థన)
వేర్వేరు వ్యూహాలు, అభిప్రాయాలను వాదించడం
క్రిటికల్ థింకింగ్ మరియు పర్స్యూవన్ స్కిల్స్ అభ్యాసం
4. Telephone Game / Chinese Whispers (టెలిఫోన్ గేమ్)
ఒక లైన్ లో విస్తరించిన సందేశాన్ని ఫిజికల్ వాయిస్ లో వెనకకు చెప్పడం
లిసనింగ్ మరియు క్లారిటీ నేర్చుకోవడం
5. Charades with a Twist (చారేడ్స్ గేమ్)
పదాలు లేదా వాక్యాలను అధికంగా nonverbal గా అద్భుతంగా చూపించడం
నాన్వెర్బల్ కమ్యూనికేషన్ అభ్యాసం
6. Interview Role Play (ఇంటర్వ్యూ రోల్ ప్లే)
ఇంటర్వ్యూ ప్రశ్నలకు ప్రాక్టీస్ చేయడం
కన్వర్షేషనల్ మరియు ఫార్మల్ స్పీచ్ స్కిల్స్ అభ్యాసం
7. Picture Storytelling (ఫోటో ద్వారా కథ చెప్పడం)
చిత్రాలను ఉపయోగించి కథ చెప్పడం
డిస్క్రిప్టివ్ లాంగ్వేజ్ మరియు ఇమాజినేషన్ పెంపొందించడం
8. Stand Up for Fillers (ఫిల్లర్ వర్డ్స్ తగ్గించడం)
టాపిక్ పై మాట్లాడేటప్పుడు “um, ah” వంటి ఫిల్లర్స్ ఉపయోగించకూడదు
ప్రీసైజ్ మరియు ఎఫెక్టివ్ లాంగ్వేజ్ అభ్యాసం
9. Listening and Following Directions Games (లిసనింగ్ మరియు డైరక్షన్స్ ఫాలో చేయడం)
Blindfold Instructions వంటి గేమ్స్
వర్బల్ గైడెన్స్ మరియు లిసనింగ్ స్కిల్స్ అభ్యాసం
10. Emotion and Expressive Reading (భావోద్వేగంతో చదవడం)
వాక్యాలను వేరే వేరే ఎమోషన్స్ తో చదవడం
ఎమోషనల్ ఇంటెలిజెన్స్ మరియు ఎక్స్ప్రెసివ్ స్పీచ్ అభ్యాసం
15) పిల్లల ఆర్ధిక (early) స్పీచ్ అభివృద్ధికి తల్లిదండ్రుల పాత్ర మరియు భాగస్వామ్యం
పిల్లల మాటలు మరియు భాషా అభివృద్ధిలో తల్లిదండ్రుల పాత్ర అత్యంత కీలకమైనది. వారు అందించగల ముఖ్యమైన సహకారం మరియు భాగస్వామ్యం కిందివిధంగా ఉంటుంది:
సంపూర్ణ, సమాధానాత్మక భాషా ఇన్పుట్ ఇవ్వడం
పరస్పర సంబంధాలు మరియు meaningful interactions లో పాల్గొనడం
Book reading, storytelling, conversational games లాంటి learning activities లో స్వయంగా పాల్గొనడం
స్పీచ్ థెరపీ టెక్నిక్స్ను ఇంట్లో reinforcing చేయడం
—
తల్లిదండ్రుల కీలక పాత్రలు మరియు భాగస్వామ్యం
1. స్పీచ్ పరిమాణం మరియు నాణ్యత (Quantity & Quality of Speech)
పిల్లలతో ఎక్కువ మాట్లాడటం, వివిధ, సంక్లిష్టమైన పదజాలాన్ని ఉపయోగించడం
భాషా వైవిధ్యం (richness) మాత్రమే కాదు, సంఖ్య కూడా ముఖ్యము
పిల్లల vocabulary మరియు language skills ను పెంచుతుంది
2. సమాధానాత్మక పరస్పర సంబంధాలు (Responsive Interactions)
పిల్లల వాక్యాలు, హావభావాలు, జెస్టులు కి తక్షణ స్పందించడం (“serve and return”)
సానుకూల, చురుకైన పరస్పర సంబంధాలు సక్రియ కమ్యూనికేషన్ అభివృద్ధికి సహాయపడతాయి
3. రొటీన్ లెర్నింగ్ Activities (Routine Learning Activities)
Book reading, storytelling, conversational engagements లో పాల్గొనడం
Vocabulary, comprehension, literacy skills పెరుగుతాయి
భాషా మరియు చదువుదారుల (literacy) క్షేత్రానికి స్థిరమైన పునాది
4. స్పీచ్ థెరపీ లో తల్లిదండ్రుల పాల్గొనడం (Parental Involvement in Speech Therapy)
ఇంట్లో దైనందిన రొటీన్ లో థెరపీ టెక్నిక్స్ ప్రాక్టీస్ చేయడం
ఇది పిల్లల అభ్యాసం మరియు ప్రగతిని వేగవంతం చేస్తుంది
తల్లిదండ్రుల ఆబ్జర్వేషన్స్ మరియు ఫీడ్బ్యాక్, థెరపీని మరింత సమర్ధవంతంగా రూపొందించడానికి ఉపయోగపడతాయి
5. తండ్రుల పాత్ర (Father’s Role)
ప్రత్యేకంగా infancy దశలో తండ్రుల భాషా ఇన్పుట్
expressive language development లో ప్రత్యేక సహాయం
తల్లిదండ్రుల (పితృమాతృ) సహకారాలు కలిసినప్పుడు కమ్యూనికేషన్ అవుట్కమ్స్ మెరుగవుతాయి
16) పిల్లల్లో ఆర్ధిక (early) స్పీచ్ ఎప్పుడు మొదలవుతుంది?
వ్యాఖ్య:
పిల్లల్లో స్పీచ్ అభివృద్ధి సుమారుగా 6 నెలల వయసులో ప్రారంభమవుతుంది, ఇంతకుముందు babbling sounds (“ooh,” “aah,” “ba-ba”) వినిపిస్తాయి.
పిల్లలు సాధారణంగా మొదటి అర్థపూర్వక పదాలు 12–18 నెలల వయసులో పలకడం ప్రారంభిస్తారు.
12 నెలలకు కొంతమంది పిల్లలు “ma-ma” లేదా “da-da” అంటారు.
18–24 నెలల మధ్య, చిన్నవారులు రెండు నుండి మూడు పదాలతో సింపుల్ ఫ్రేసెస్ తయారు చేయడం ప్రారంభిస్తారు.
2 ఏళ్ళకు వాక్యజాలం 50+ పదాలు చేరుతుంది.
3 ఏళ్ళకు మూడ్–నాలుగు పదాల వాక్యాలు ఉపయోగించి, పరిచయమైన వ్యక్తులు వారిని సులభంగా అర్థం చేసుకుంటారు.
—
Early Speech Milestones (ప్రారంభ స్పీచ్ మైలురాళ్ళు)
1. జననం – 3 నెలలు:
Cooing sounds, వాయిస్ కు స్పందించడం, నవ్వు లేదా ఫస్సింగ్ వంటి శబ్దాలతో భావాలను వ్యక్తీకరించడం
2. 4 – 6 నెలలు:
Babbling ప్రారంభం (“ba-ba”)
3. 7 – 11 నెలలు:
సింపుల్ పదాలను అనుకరించడం, babbling కొనసాగించడం
4. 12 – 18 నెలలు:
మొదటి అర్థపూర్వక పదాలు (“mama,” “dada”)
5. 18 – 24 నెలలు:
రెండు నుండి మూడు పదాలతో ఫ్రేస్లు ప్రారంభం
6. 2 ఏళ్ళ వయసు:
Vocabulary సుమారుగా 50+ పదాల వరకు పెరుగుతుంది
7. 3 ఏళ్ళ వయసు:
మూడు–నాలుగు పదాల వాక్యాలు ఉపయోగించడం, పరిచయ వ్యక్తులు అర్థం చేసుకోవడం
18) Autism, ADHD, MR, మరియు Down Syndrome పిల్లల్లో స్పీచ్ డిలే కారణాలు
వ్యాఖ్య:
Autism, ADHD, మానసిక మందగమన (MR), లేదా Down Syndrome ఉన్న పిల్లలు వివిధ న్యూరోలోజికల్ మరియు అభివృద్ధి సంబంధిత కారణాల వల్ల ఆలస్యంగా మాట్లాడవచ్చు లేదా అసలు మాట్లాడకపోవచ్చు.
—
1. Autism లో:
కారణాలు:
సోషల్ కమ్యూనికేషన్ లో సమస్యలు
నాన్-వర్బల్ cues అర్థం చేసుకోవడంలో కష్టాలు
భాషా ప్రాంతాల atypical brain development
లక్షణాలు:
మాట్లాడే భాష ఆలస్యం లేదా లేమి
Echolalia (పదాలు/వాక్యాలను మళ్లీ చెప్పడం)
మోనోటోనస్ లేదా రోబోటిక్ స్పీచ్
సహాయం:
Speech and Language Therapy (SLT)
కొంతమంది పిల్లలు non-verbal లేదా minimally verbal గా ఉంటారు
—
2. ADHD లో:
కారణాలు:
Attention deficits వల్ల భాష నేర్చుకోవడంలో అంతరాయం
Hyperactivity మరియు impulsivity వల్ల స్పీచ్ అలవాట్లపై ప్రభావం
లక్షణాలు:
సాధారణంగా స్పీచ్ డిలే Autism లేదా Intellectual Disability కంటే తక్కువ
కమ్యూనికేషన్ సమస్యలు కొద్దిగా మాత్రమే
—
3. Mental Retardation / Intellectual Disability (MR) లో:
కారణాలు:
Cognitive development లో లోపం, భాష అర్థం చేసుకోవడంలో సమస్య
లక్షణాలు:
Vocabulary పరిమితం
Sentence formation లో కష్టం
Cognitive level కు తగినట్లుగా భాషా అభివృద్ధి ఆలస్యంగా
—
4. Down Syndrome లో:
కారణాలు:
Oral motor skills లో low muscle tone
Hearing loss
Cognitive delay
లక్షణాలు:
స్పీచ్ ఆలస్యంగా మొదలవుతుంది
స్పష్టంగా శబ్దాలు పలకడంలో కష్టం
verbal communication పరిమితం
19) Speech Delay ఉన్న పిల్లలకు, Speech Therapy కావాలా లేదా సాధారణ స్కూలింగ్ మాత్రమే సరిపోతుందా?
సారాంశం:
Speech Therapy అనేది సాధారణ స్కూలింగ్ (mainstream schooling) కంటే ఎక్కువ ముఖ్యంగా ఉంటుంది, ఎందుకంటే ఇది పిల్లల ప్రత్యేక కమ్యూనికేషన్ అవసరాలను లక్ష్యంగా పెట్టుకొని నేరుగా పరిష్కరిస్తుంది, అది తరగతిలో సాధారణంగా అందదు.
—
Speech Therapy ఎందుకు ముఖ్యమో:
1. వ్యక్తిగత సమస్యకు సరిపడే థెరపీ
Articulation, expressive/receptive language, apraxia, stuttering, voice issues లాంటి ప్రత్యేక సమస్యలకు tailored diagnosis & treatment plan ఇవ్వబడుతుంది
సాధారణ క్లాసులు ఇంత లోతుగా ఇవ్వలేవు
2. ఆరంభ, లక్ష్యపూర్వక పరిష్కారం (Early intervention)
Preschool సంవత్సరాల్లో Brain & Language Development వేగంగా జరుగుతుంది
తర్వత భాషా మరియు చదువుదారుల (literacy) ఫలితాలు మెరుగవుతాయి
3. నిర్వచనాత్మక ఫలితాలు (Clinical evidence)
Phonological, vocabulary deficits లాంటి సమస్యలలో measurable gains వస్తాయి
Classroom exposure మాత్రమే ఈ గ్యాప్ ను తగ్గించలేని పరిస్థితులు ఉంటాయి
—
సాధారణ స్కూలింగ్ మాత్రమే ఉన్న పరిమితులు:
1. తరగతి సోషల్ మోడల్స్ మరియు భాష exposure ఇస్తుంది
2. కానీ frequency, intensity, individualized methods లేకపోవడం వల్ల significant speech delay ఉన్న పిల్లలకు clinical progress తక్కువ
—
Recommended Best-Practice Approach:
1. Speech Therapy + Inclusive Schooling కలపడం
Formal SLP evaluation
Individualized therapy (clinic, school-based, or integrated)
Classroom supports: IEP/accommodations, visual aids, small-group pull-outs
2. Early Start & Regular Monitoring
ఇంట్లో caregivers భాగస్వామ్యం (home practice)
Parent-implemented strategies, clinician-delivered strategies కు సమాన ఫలితం ఇవ్వగలవు
3. Specialist Support
Mainstream schools adequate support ఇవ్వకపోతే
Specialist provision లేదా extra therapy hours until functional communication & academic readiness
—
Practical Next Steps:
1. SLP Evaluation: సమస్యల రకం మరియు తీవ్రత తెలుసుకోవడానికి
2. School Evaluation & IEP: Direct SLP time, classroom accommodations
3. Home Strategies:
Modeling, expanded language, play-based routines
Regular progress reviews
19) Speech Delay ఉన్న పిల్లలకు, Speech Therapy కావాలా లేదా సాధారణ స్కూలింగ్ మాత్రమే సరిపోతుందా?
సారాంశం:
Speech Therapy అనేది సాధారణ స్కూలింగ్ (mainstream schooling) కంటే ఎక్కువ ముఖ్యంగా ఉంటుంది, ఎందుకంటే ఇది పిల్లల ప్రత్యేక కమ్యూనికేషన్ అవసరాలను లక్ష్యంగా పెట్టుకొని నేరుగా పరిష్కరిస్తుంది, అది తరగతిలో సాధారణంగా అందదు.
—
Speech Therapy ఎందుకు ముఖ్యమో:
1. వ్యక్తిగత సమస్యకు సరిపడే థెరపీ
Articulation, expressive/receptive language, apraxia, stuttering, voice issues లాంటి ప్రత్యేక సమస్యలకు tailored diagnosis & treatment plan ఇవ్వబడుతుంది
సాధారణ క్లాసులు ఇంత లోతుగా ఇవ్వలేవు
2. ఆరంభ, లక్ష్యపూర్వక పరిష్కారం (Early intervention)
Preschool సంవత్సరాల్లో Brain & Language Development వేగంగా జరుగుతుంది
తర్వత భాషా మరియు చదువుదారుల (literacy) ఫలితాలు మెరుగవుతాయి
3. నిర్వచనాత్మక ఫలితాలు (Clinical evidence)
Phonological, vocabulary deficits లాంటి సమస్యలలో measurable gains వస్తాయి
Classroom exposure మాత్రమే ఈ గ్యాప్ ను తగ్గించలేని పరిస్థితులు ఉంటాయి
—
సాధారణ స్కూలింగ్ మాత్రమే ఉన్న పరిమితులు:
1. తరగతి సోషల్ మోడల్స్ మరియు భాష exposure ఇస్తుంది
2. కానీ frequency, intensity, individualized methods లేకపోవడం వల్ల significant speech delay ఉన్న పిల్లలకు clinical progress తక్కువ
—
Recommended Best-Practice Approach:
1. Speech Therapy + Inclusive Schooling కలపడం
Formal SLP evaluation
Individualized therapy (clinic, school-based, or integrated)
Classroom supports: IEP/accommodations, visual aids, small-group pull-outs
2. Early Start & Regular Monitoring
ఇంట్లో caregivers భాగస్వామ్యం (home practice)
Parent-implemented strategies, clinician-delivered strategies కు సమాన ఫలితం ఇవ్వగలవు
3. Specialist Support
Mainstream schools adequate support ఇవ్వకపోతే
Specialist provision లేదా extra therapy hours until functional communication & academic readiness
—
Practical Next Steps:
1. SLP Evaluation: సమస్యల రకం మరియు తీవ్రత తెలుసుకోవడానికి
2. School Evaluation & IEP: Direct SLP time, classroom accommodations
3. Home Strategies:
Modeling, expanded language, play-based routines
Regular progress reviews
20) ADHD & Autism పిల్లల్లో స్పీచ్ సమస్యల ప్రధాన కారణాలు
వ్యాఖ్య:
ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) మరియు Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) లో స్పీచ్ సమస్యలు సాధారణంగా ఉంటాయి, కానీ ప్రతి పరిస్థితికి ప్రత్యేక కారణాలు మరియు లక్షణాలు ఉంటాయి.
—
ADHD లో స్పీచ్ సమస్యల కారణాలు:
1. Core ADHD లక్షణాలు: Inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity
2. Auditory Attention లో తగ్గుదల: మాటలను అర్థం చేసుకోవడంలో మరియు ఉత్పత్తి చేయడంలో కష్టం
3. Hyperactivity: టోన్ తేడాలు, ఎక్కువ శబ్దం, వేగవంతమైన స్పీచ్, తప్పుగా ఉచ్ఛరించడం, disfluencies
4. Impulsivity: social communication లో సమస్యలు (interruption, excessive talking, turn-taking కష్టం, non-verbal cues అర్థం చేసుకోవడం లో కష్టం)
5. ఫలితాలు:
Speech clarity సమస్యలు
Thoughts organization లో కష్టం
Pragmatic language difficulties (topic maintain చేయడం, conversational rules అర్థం చేసుకోవడం)
—
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) లో స్పీచ్ సమస్యల కారణాలు:
1. Neurological differences: social interaction, communication, behavior పై ప్రభావం
2. Conversation challenges: ప్రారంభించడం మరియు sustain చేయడంలో కష్టం
3. Nonverbal communication లో కష్టం: facial expressions, gestures, intonation సరిగ్గా ఉపయోగించలేకపోవడం
4. Repetitive/fixated speech patterns, eye contact లో కష్టం
5. Pragmatic language issues: turn-taking, social cues అర్థం చేసుకోవడం కష్టం
6. Neural connectivity లో లోపం: articulation మరియు reciprocal communication సమస్యలు
—
ADHD + Autism co-occurrence:
ADHD impulsivity Autism repetitive speech patterns ను పెంచవచ్చు
Interactions మరింత కష్టతరం అవుతుంది
—
Therapeutic Approaches:
Personalized speech therapy
Behavioral strategies
Sensory integration strategies
Communication effectiveness మెరుగుపరచడానికి
1.2 ) 1-year-old బిడ్డ మాట్లాడే సాధారణ పదాలు
A) సాధారణ పదాలు:
ఒక 1-సంవత్సర బిడ్డ సాధారణంగా సులభమైన మరియు పరిచయమైన పదాలను చెబుతుంది. సుమారు 12 నెలల వయసులో, బిడ్డలు ఒకటి లేదా రెండు పదాలు చెబుతారు, ఉదా: “మామా,” “డాడా,” “హాయ్,” “బై,” “డాగ్,” “అహ్-ఓ”.
ఈ పదాలు ఎప్పుడూ పూర్తిగా స్పష్టంగా ఉండకపోయినా, బిడ్డకు ముఖ్యమైన వ్యక్తులు, వస్తువులు లేదా సంఘటనలను సూచిస్తాయి.
మిగతా సాధారణ పదాలు:
పరంపర పేర్లు: మామా, డాడా, పాపా
సామాజిక పదాలు: హాయ్, బై, కాదు, అహ్-ఓ
వస్తువుల పేర్లు: బంతి, కుక్క, బేబీ, బాటిల్, బనానా
ప్రాణి శబ్దాలు: వూఫ్ వూఫ్, మూ
ప్రతి-సమయంలో అర్థం ఉన్న సాధారణ శబ్దాలు: బా-బా (బాటిల్), నానా (బనానా)
ఈ వయసులో, సంవాదం పదాలు, శబ్దాలు, మానవ చలనాల మిశ్రమంగా ఉంటుంది. బిడ్డలు భాషను అర్థం చేసుకోవడం, తమ భావాలను వ్యక్తపరచడం ప్రారంభిస్తారు.
In 2021, Autism Little Plant launched its Inclusive Education Programme for special children. Initially, therapy services like speech, behaviour, and occupational therapy were offered to children with severe and moderate difficulties. Once progress was achieved, they were gradually integrated into government schools alongside normal children. This approach promoted socialization, communication, acceptance, and cooperation. Since 2021, every Monday to Friday, Autism Little Plant children have been participating in inclusive classroom activities, fostering growth and understanding.

We are the experts in finding the proper reason for your symptoms and First ever center established by American Doctors in India to offer cutting-edge advanced treatment for Vertigo, Dizziness, and other balance disorders.
RASYA Indo-American Clinic is India’s First state-of-the-art center with American standards providing complete hearing health care solutions personalized for both pediatrics and adults.
Frustrated with ringing in your ears? Our contemporary American Standard protocols are specifically designed for each of you to bring back peace in your life.
Experience revolutionary American hearing technology, expertly programmed by US-trained specialists, at our state-of-the-art infrastructure designed for best hearing.
We are developing advanced Vestibular Rehabilitation program, please visit back soon or contact us to get notified.
Delivered by US‑trained professionals and designed for families. Our play‑based, data‑driven program integrates Speech Therapy, AVT, Autism, OT, Behavioral/ABA, and Special Education—so your child progresses faster, happier, and with you involved at every step.
At Monaplay Child Develepment Society, we’ve transformed the lives of thousands of patients suffering from long-term vertigo, dizziness, Tinnitus, Hearing Loss and Speech Disorders. Our success is reflected in the heartfelt testimonials of our clients who have regained control of their lives.




Schedule your consultation appointment today with our International Specialists.